CDN
Why do we need CDN?
The main purpose of a Content Delivery Network (CDN) is to reduce latency, or the communication delay caused by network design. Due to the global scale and complexity of the internet, communication traffic between websites (servers) and their users (clients) must traverse long physical distances. Communication is also two-way, with requests sent from clients to servers and responses returned from servers.
CDN improves efficiency by introducing intermediate servers between clients and website servers. These CDN servers manage some of the communication between clients and servers. They can reduce web traffic to the web server, decrease bandwidth consumption, and improve the user experience of applications.
For more information on CDN, see an introduction from AWS: What is CDN (Content Delivery Network)?
Here's a diagram to illustrate the difference between using and not using CDN services:
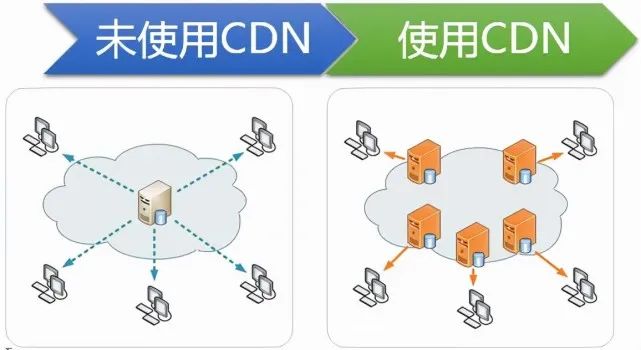
CDN services require a domain name. Please apply for a domain name first. Note that for CDN configuration in mainland China, the domain name must be filed, while overseas domain names may not need to be filed.
Setting up CDN
Tencent Cloud
See the documentation for specifics: Configuring CDN Domain Names
Alibaba Cloud
See the documentation for specifics: Using CDN to Accelerate the Delivery of Images in OSS.
AWS
See the documentation for specifics: Deliver Content Faster with Amazon CloudFront。
The CDN service from AWS is called CloudFront.